No products in the cart.

Whether you are a new business owner or one just buying a new POS system, there are several things for you to consider. From developing a business plan to setting up the store, you’ve got a lot on your plate. But one of the most important decisions you need to make is choosing the right POS system for your business.
Decades ago, a Point of Sale (POS) system could only perform basic cashiering functions.
Nowadays, with advancements in technology, artificial intelligence and data, POS systems are more than just a point of sale; they are a point of management. But with these new advanced features and so many different POS systems available on the market comes a lot of confusion on what everything is and what it can do. Which POS system is right for you?
If you’re a small business owner or large corporation opening a new store or looking for a POS system, we’ve put together a comprehensive guide that’ll take you through everything you need to know. From what a POS system is, the types of systems available, the hardware and software and some FAQs that you need to know before buying a POS system, you’ll be a pro in no time!
A Guide to Point of Sale (POS) Systems
1. What is a POS system?

A POS system (or Point of Sale system) is a type of computerised system that is commonly found in retail, F&B and hospitality businesses in order to conduct transactions. Acting as a hub for your business, it seamlessly integrates all sales, inventory, customer, employee, and more information into one single system.
A POS system is composed of hardware and software that allows you to perform sales transactions, track inventory, create loyalty programs and promotions, generate reports and analyse data. If you’ve ever seen a POS system in any store, you may have seen some of the many hardware components involved in running the business. Peripherals like monitors, a cash register, barcode scanner, receipt printer and more help you print receipts, scan barcodes, accept multiple types of payments, and store cash among other things.
2. What is the difference between a cash register and a POS system?
If you’ve ever worked at or visited any retail store or restaurant before, you’ve probably seen cash registers and POS systems. And yes, there is an obvious difference in appearance. However, appearances aside, there are a lot more differences between the two than meets the eye. While they are both used to process transactions, there are several key differences that separate them.
Here’s a handy infographic about what makes a POS system different from a cash register.

With limited customisability, cash registers are a single-function device whose primary purpose is to record transactions and calculate the total amount of cash due. They also only track transactions in real-time with no way of storing or analysing historical data. However, this does mean that they are typically cheaper than POS systems.
In contrast, Point of Sale systems are a computerised system that offers a vast range of functions that are beyond simple transactions. These include inventory management, enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer and employee management, and more. A POS system also has a greater capacity for storing and analysing transactional data, providing you with valuable insights into your sales data and customer behaviour. With greater customisability, POS systems can be tailored to your specific business needs.
The simplicity and low cost of cash registers can make them useful in certain situations; however, they have been largely replaced by more advanced POS systems in most businesses. If you want to manage your entire business with only one system, a POS system may be the right option for you.
Explore more in this in-depth article about the differences between cash registers and POS systems.
3. Are there different types of POS systems?
Every business has its own needs and requirements for a POS system, so yes, there are different types of POS systems. There are six main types of POS systems that businesses use: legacy, cloud-based, tablet, mobile, self-service and multichannel. Each one has its own advantages and disadvantages, so when you are choosing a POS system that is suitable for your business, there is much to consider. However, while there are differences between them, do note that there is still a lot of overlap in what these systems offer.
a. Legacy
Legacy, traditional or on-premise POS systems differ from other systems by saving data locally, usually only on a single device or multiple devices connected in a closed internal network. This limits customer data, transactions and other information to within the closed network or primary allocated device; thus, it provides strong security and prevents loss of data or system affected issues when the internet is down.
Legacy systems are often familiar to employees, reducing the learning curve for training, and they can also be highly customised to your business needs. Unlike cloud-based systems, they don’t require internet connection to function.
However, Legacy POS systems tend to run on POS provider-specific hardware, which means integrations with other systems or transferring data to a different POS solution becomes more difficult. Furthermore, ongoing maintenance can be expensive and even non-existent once the POS terminal gets outdated. The software must also be manually updated, and may not have the latest features required by most businesses to operate efficiently.
B. Cloud-based POS
Cloud-based POS systems store and process data on remote servers in the cloud, rather than on a local device or network. Provided that you have an internet connection, this affords you the ability to access and alter company data from anywhere and through any device, without the need for local storage.
Most modern POS systems are predominantly cloud-based, ensuring up-to-date technology with frequent and automatic software updates and new features. As such, a cloud-based POS system can be easily scaled up or down as your business grows and your needs change. All data is also synchronised, which is highly useful when you have multiple locations and online websites through which you are generating sales. Additionally, built-in encryption and security measures provide robust security to protect your sensitive data.
How does it work? When a sale is made, the details are keyed into the POS terminal and then transmitted to the cloud-based servers via the internet to be stored and processed. Data can be retrieved from any device with an internet connection, allowing you to monitor sales and inventory in real-time.
As the main two types of POS systems, you may want to know more about them. Check out the infographic to learn the differences between legacy and cloud-based systems.


C. Tablet
With increasing demand for portability and mobile convenience, Tablet POS systems have been gaining popularity. As iPad and Android Point of Sale solutions require minimal upfront investment while maintaining some level of sophisticated support such as inventory management and tracking of employee time, they are often the main POS system of choice for mobile vendors, quick-service restaurants, coffee shops, gift shops and more. The learning curve also tends to be easier since the system runs on hardware many people are familiar with, making training and onboarding easier. Many tablet POS system vendors support compatible hardware, including tablet supports, cash drawers, and barcode readers.
D. Mobile
Mobile Point of Sale systems are designed to be portable, wireless POS systems that utilise smartphones and tablet services to process transactions. As they are lightweight, compact and easy to use, they are ideal for pop-up stores, outdoor events or any businesses that need to process payments on the go.
How does it work? A mobile POS system works by entering transaction information such as total sale prices and items purchased into the device where payments are then processed. In many cases, they are equipped with a card reader to take cashless payments in a secure, encrypted manner. Like a normal POS system, mobile pos systems can process payments, do inventory management and provide customer management. They also allow for increased flexibility, faster checkout times, and reduced costs. You can also view real-time sales and inventory data, to make better decisions on the fly.
E. Self Service Kiosk
Self-service kiosks are specialised solutions designed to fulfil a more specific purpose. As an automated terminal, it has no need for employee interaction and so customers can view information and perform transactions at their convenience. With quick access to information, self-service kiosks are designed to be user-friendly for mass usage, allowing your business to reduce wait times and human error, and improve customer service. They typically include a touchscreen interface, card reader, receipt printer and other hardware necessary to perform the required functions.
How does the self-service kiosk work? Customers interact with the kiosk to select items, enter payment information and print receipts, completing the transaction. Upon completion, the order is transferred to the POS system which processes the data and updates the inventory and sales records accordingly.
These kiosks are commonly found in retail stores, quick-service restaurants, airports, banks, hospitals and more. For example, quick service restaurants – such as McDonald’s – have self-service kiosks so customers can order their food and pay without going to a cashier. Movie theatres also provide a self-service kiosk where customers can buy movie tickets, whereas retail kiosks may show prices and product availability. Accepting employment applications, hospital patient check-ins and human resources are a few additional uses.
F. Multichannel
Multichannel POS systems are Point of Sale systems that allow businesses to manage sales and business data across multiple sales channels like brick-and-mortar stores and e-commerce websites. They are extremely advantageous for businesses who sell across many online or physical locations. These systems provide a single, unified view of all sales, inventory and customer data across channels, enabling better operations management and customer service.
How does a multichannel POS work? When transactional data is entered into the system through your various channels, the POS system synchronises this data in real-time. Hence, you will have a better idea of your inventory levels for all channels and be able to restock to ensure that there is enough stock. With one view for all channels, you can have a better understanding of how your business is performing in its entirety.
4. What are the different parts of a POS system?
If you are getting a new POS system, it’s important to make sure you have the appropriate hardware for your business needs. Depending on your industry and business-specific requirements, your POS system hardware may differ from others. As you evaluate your point-of-sale setup options, you’ll want to know what hardware your POS system can have.
Here are some of the hardware parts that a POS system can have:

A. Touchscreen Terminal
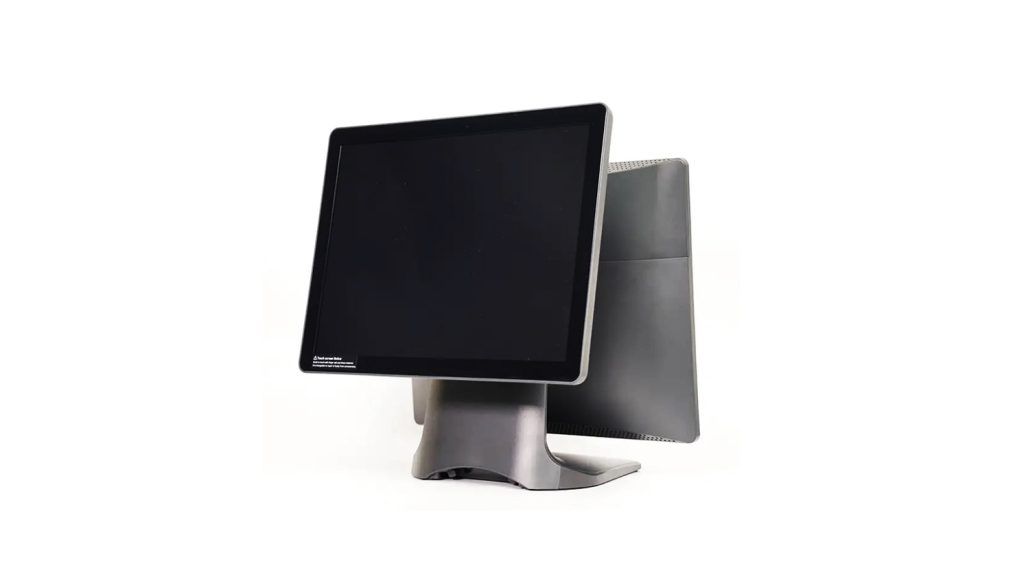

The touchscreen terminal is your main point of contact when using the POS system. It allows your cashiers to access the frontend POS system’s software features and run the business. You can ring up customers, view customer details, set appointments, start and end shifts, and perform daily sales and cashiering operations.
B. Customer Display
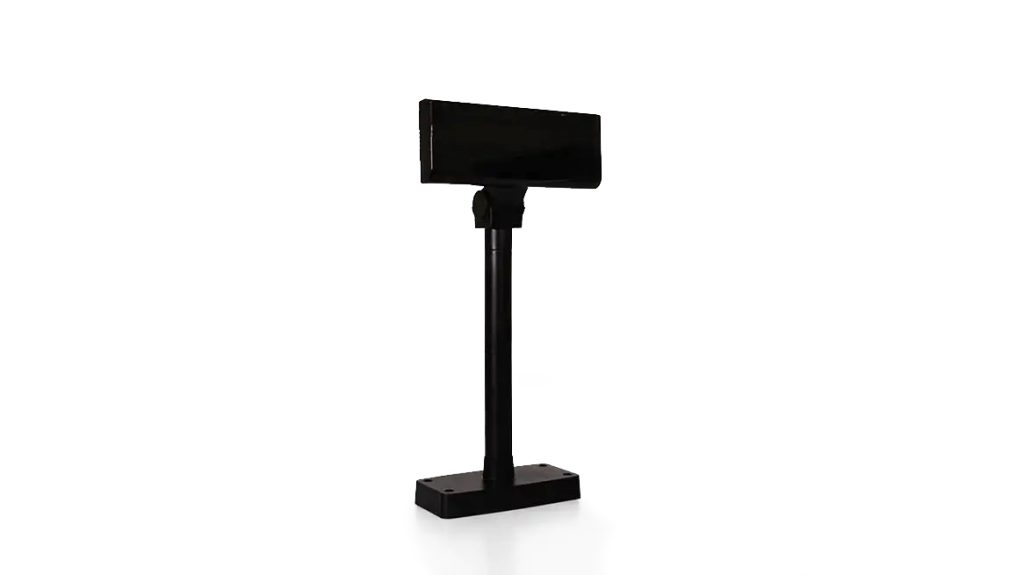


The customer display allows the customer to see what is being transacted and the amount they have to pay. There are two types of customer displays: a simple text display and a full screen display. The simple customer display projects the price of each item as they are rung up and then the total amount due. However, like the touchscreen terminal on the cashier’s side, the customer’s full screen display shows the full receipt of items, the amount owed and depending on the integrations, QR codes for mobile payment methods.
C. Cash Drawer
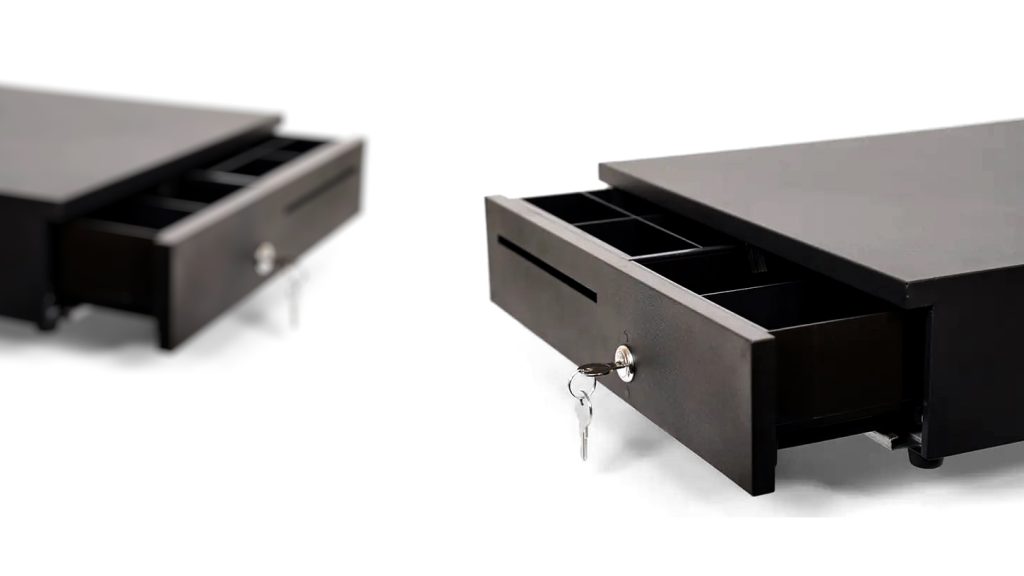

When processing payments, you may need a secure place to store your cash; hence, the cash drawer which is used to store cash, coins and other currency transacted from customers. To keep your sales secure, the cash drawer is connected to your receipt printer and will open only when a cash sale is processed in the POS system and the receipt is printed. However, you can opt to not print a receipt if the customer does not want it. With POS software, you are also able to minimise theft and fraud by connecting your entire system to the cash drawer, and tracking when and how many times the drawer is opened.
D. Receipt Printer
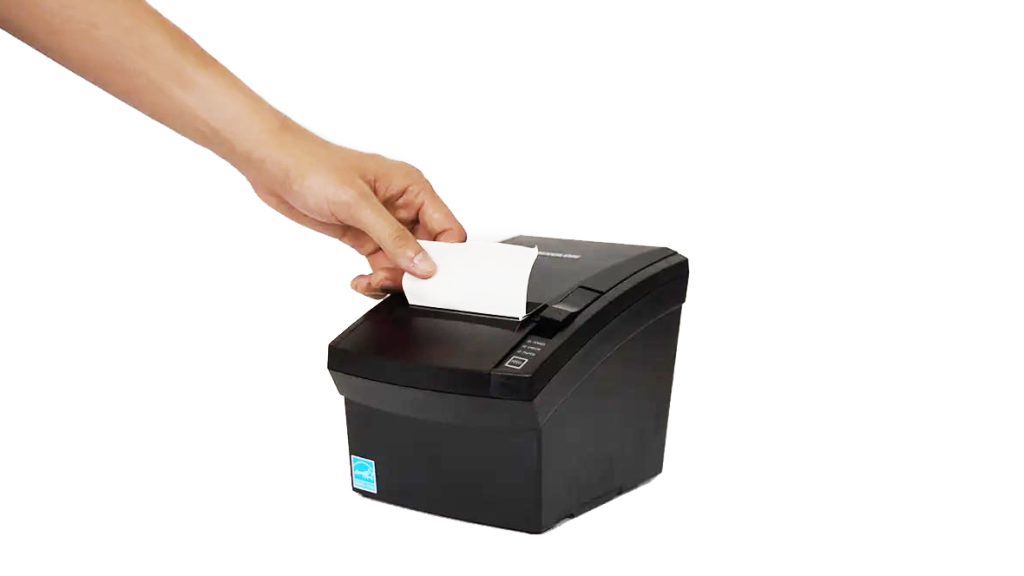

Despite our trajectory towards digitalisation, some people still prefer to have a printed receipt. The receipt printer provides customers with a record of what they have purchased, when they purchased it, and how much they paid. Most receipt printers use thermal printing with grayscale or limited colour options.
E. Multi-Angle Ball Scanner
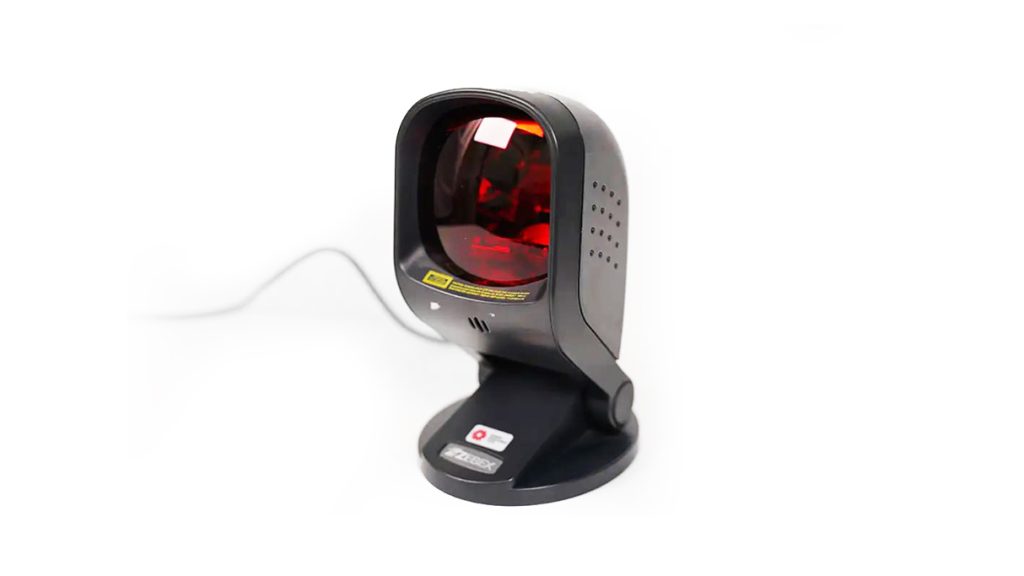

A multi-angle ball scanner, or an omnidirectional scanner, is a type of barcode scanner that uses laser scanning to detect barcodes. This allows your cashiers to send an item’s details digitally to the POS system, ring it up, and check the price, inventory stock level and more detailed information. Since it is designed to scan from multiple angles, it improves the speed and accuracy of scanning.
F. Handheld Scanner
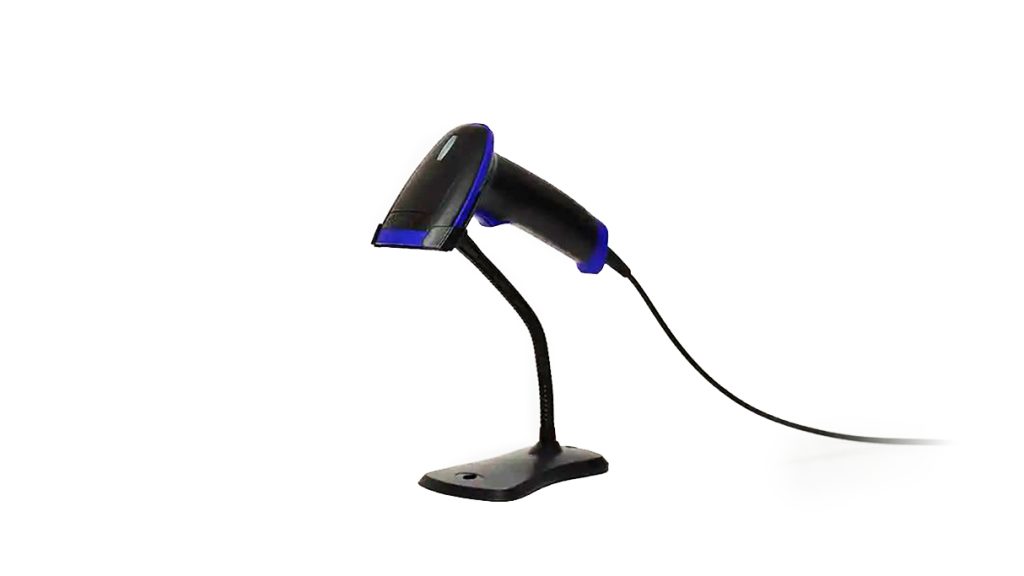

The handheld scanner is also a type of barcode scanner like the muli-angle ball scanner, but instead of using lasers, it uses image scanning to detect the barcode image. It provides real-time information about price, stock levels and other digital information about a certain product. Due to its design, it is also portable and flexible, enhancing the speed at which you can scan products.
G. Barcode Printer
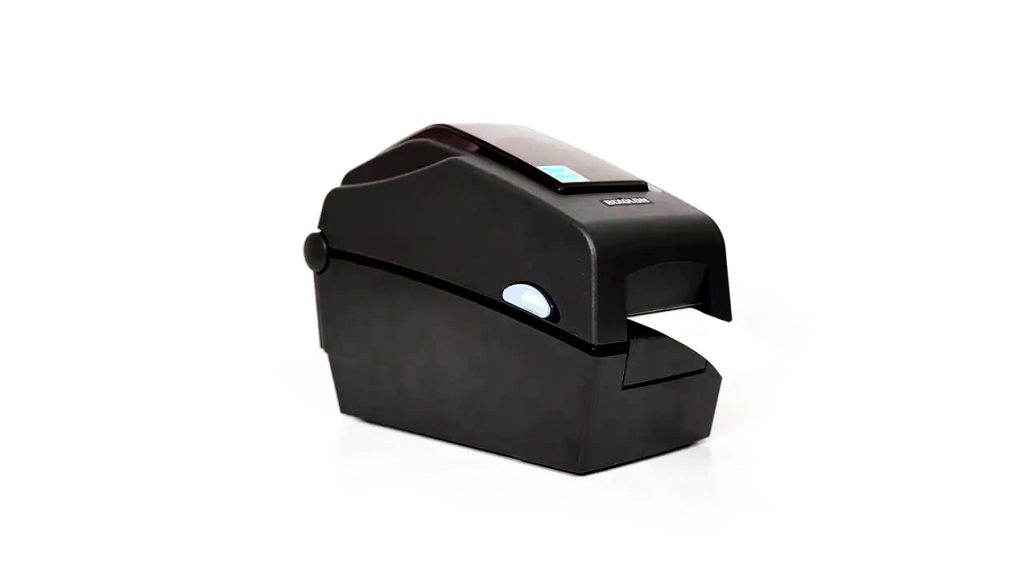

The barcode printer allows you to print and add relevant barcode stickers and hence, product information, to a specific product. With an internal barcoding and SKU number label system that lets you sort by category, vendor and more, you can organise and track inventory a lot easier.
H. Handheld Stock Scanner
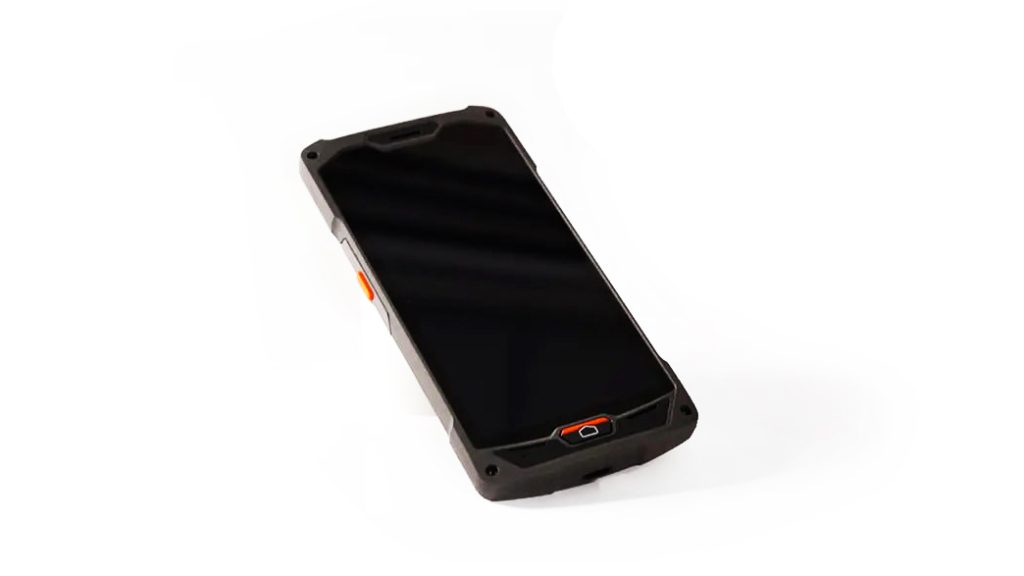

In regards to tracking and managing inventory, a handheld stock scanner can be one of your most useful tools. With the ability to scan barcodes easily and flexibility, they can keep track of your inventory, and hence, collect and update data in the linked POS system in real-time. When you use the handheld stock scanner to regularly scan products, you can reconcile the actual stock levels with the recorded amount in your inventory management system.
I. Kitchen Printer & Kitchen Display
For F&B businesses, the POS system can have a few extra peripherals that can help you run your restaurant seamlessly. The POS system can send purchase orders directly to the kitchen printer where they will then be printed out using smudge-proof impact printing for the kitchen staff to then prepare. Additionally, they can also come with colour options to make any modifiers or allergies stand out. In cases where you aren’t using a digital kitchen display system (KDS), these kitchen printers can help your kitchen work more efficiently.
Kitchen display systems are a viable way of sending order information through the POS system to the kitchen immediately upon ordering. These systems can not only preview orders, but also prioritise and separate orders by course for both offline and online orders. This quickens the time it takes for orders to reach the kitchen and reduces errors. You may also choose to print out the orders, of course.
5. What features does a POS system have?
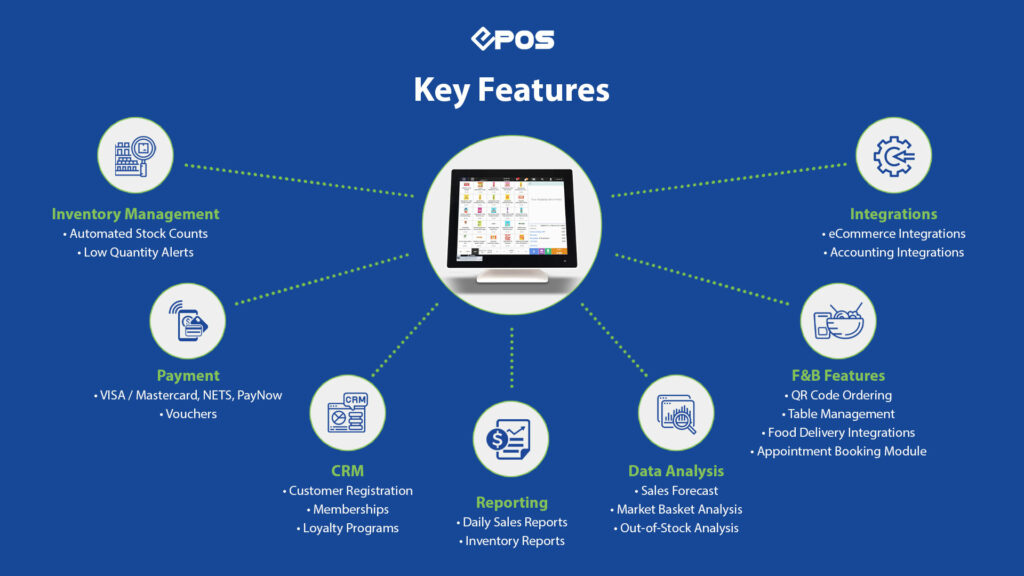
While hardware options are generally consistent across POS systems, POS systems vastly differ in the software that they offer. Here, you will have to carefully evaluate your own business needs and consider which features will fulfil those needs. To get you started, here are some of the most essential software features POS systems can have.
A. Sales Transactions
The primary function of a Point of Sale system is to perform sales transactions. The basic explanation of this is that a customer chooses to purchase some items, the POS system calculates the total price which the customer then pays, and the POS system finishes the transaction.
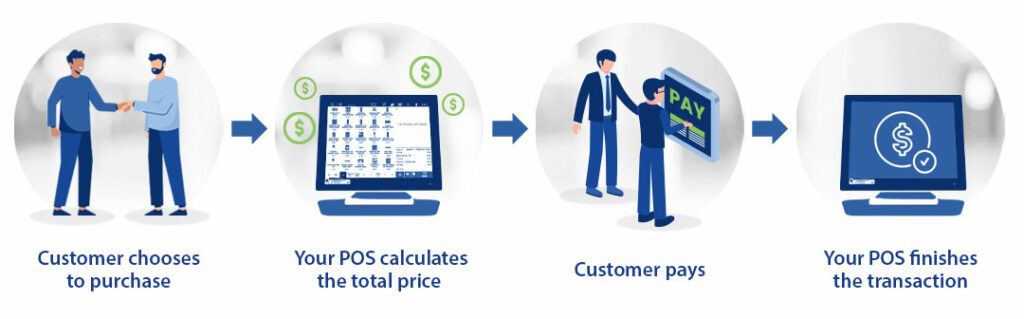
The primary function of a Point of Sale system is to perform sales transactions. The basic explanation of this is that a customer chooses to purchase some items, the POS system calculates the total price which the customer then pays, and the POS system finishes the transaction.
However, what exactly constitutes a POS transaction? Read more here!
B. Payment Methods
When you go to a store, you expect to be able to pay via certain payment methods. However, when that particular payment method isn’t available, you can only choose to use another one or not purchase the item at all. In most circumstances, customers want the flexibility to purchase things with whatever type of payment they can. The easier your transaction process is, the more likely they will return to your business. Hence, having more payment options is better.
A POS system can support various payment methods like:
- Cash
- Credit/debit cards such as Visa, MasterCard, NETS
- Contactless payments such as Apple Pay and Google Pay
- Cheques
- Gift cards, vouchers and coupons
- Electronic payments through banks, PayNow, PayLah, PayPal or other online payment services
However, do note that the specific payment methods supported by your POS system vary by vendor, the needs of your business and the region. External peripherals may also be needed in order to support certain payment methods like credit card readers.
C. Inventory Management
A key part of almost any business is understanding inventory. Hence, the inventory management module on a POS system can automate tedious and time-consuming processes, as well as collecting data about your stock. Reduce human error, manpower needs and costs, and improve the accuracy of your inventory management.
Several inventory management tools can help you maximise efficiency. With a greater capacity for inventory level monitoring and easy updates from sales information, a robust inventory management system is capable of automatically updating your stock count, setting alerts, preventing out-of-stock situations and generating purchase orders based on forecast tools. Inventory reports can also allow you to easily view your inventory movement and how much stock you need in the future.
D. Customer Relationship Management
Customer relationship management (CRM) is a crucial part of growing any business. It’s important to know who your customers are so you can nurture good relationships with them, prompting customer loyalty and retention. Your POS system can help with that. With a CRM feature, the system can collect useful customer information such as their personal details and past purchases. Then, you have the freedom to create relevant promotions, re-market and build higher customer retention.
The POS system can also help you create loyalty or membership programs so you can keep track of customers and offer them value in exchange for continued loyalty. Identify your biggest spenders – VIP customers – and create exclusive rewards or promotions. Customers who know you acknowledge and treasure them will be more likely to return and spend more at your business.
E. Reporting & Data Analytics
With an increased trajectory towards data analytics being at the forefront of business, POS systems are no longer just a place for sales transactions. Your POS system can be your greatest data aggregator, enabling you to better understand your business with real-time reports and giving you actionable insights to make better business decisions.
Just through your daily business activities, your POS system can collect and analyse information about inventory status, sales trends and preferences, customer information, and projected sales and stock figures. Extract and organise your data with customisable options, or view product sales reports, inventory reports and daily sales reports for easy analysis.
A robust data analysis module can help you generate even more detailed reports, view sales forecasts, create automated upselling, provide historically relevant products at checkout and more. Get calculated potential losses due to out-of-stock situations, create bundle promotions with frequently sold products, and improve inventory management with a smart reordering tool.
F. Employee Management
For any business with employees, it’s crucial to have employee management in your POS system for logistics, performance management and security. You can keep track of who is doing what, their performance and the permissions they are granted. With a Point of Sale system and user accounts, employees are able to log in and out, marking shifts and any actions they perform on the system. Reduce the risk of internal fraud by tracking any voids, refunds and changes to bills they make as well as performance and shift timings.
G. F&B Specific Features
Take charge of your F&B business easily with F&B specific features designed to manage your kitchen, tables and orders more efficiently and effectively. As F&B businesses are different from retailers, you’ll need different features to match your requirements. With features such as QR code ordering, table management, set menus and kitchen displays, you are now able to seamlessly manage your restaurant, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
Sync your ordering system with the kitchen to efficiently manage your customers’ food orders. Speed up taking customers’ orders through QR ordering, or even integrate with food delivery platforms, and use a table booking system to create reservations.
I. QR Ordering
A QR code ordering system is a way for F&B businesses to digitise their menu and ordering process whilst improving customers’ dining experiences, retaining customisability, and speeding up your service. After linking your restaurant’s customised e-menu to your Point of Sale backend, it can be configured based on the timing and availability of stock. That way, diners can now easily access the menu via QR codes scanned on their phones, and place their orders at their convenience.
II. Table Management
Table management refers to the feature that allows you to build your own custom restaurant table layout and promptly run your restaurant from one single module. Manage occupied and reserved tables easily with colour-coded tables, and easily take orders for your current guests. You can add modifiers, notes and discounts, assign orders or hold bills for specific tables, and get a full view of your sales with table management reporting.
H. Booking Module
Making reservations is a necessity for many businesses that take appointments, such as within the F&B and service industries. A POS system can help make, cancel and manage appointments without having to manually fill in too much information, with the added bonus of acquiring customer data for improved CRM.
On the backend, POS users will also be able to see the average time spent, the maximum number of people per reservation, available booking timings and more details in order to completely customise their booking module.
I. Table Booking
If your F&B business accepts reservations, a table booking feature is highly useful to manage these reservations within the table management module. Users and customers will have access to a Booking Site where table reservations can be made, which are then displayed on the POS system table management dashboard.
II. Appointment Booking
Similar to table booking, the POS system’s booking module can be modified to create appointments instead. The customer will be able to see the available timings and slots for booking and make reservations through the Booking Site. This feature is useful for any business that allows online appointment bookings such as clinics and salons.
I. Integrations
Modern POS systems are often equipped with programmable enhancements to integrate with third-party software programs. Hence, these systems can be tailored to a business’ exact requirements to fulfil the functions necessary.
For example, many POS systems can be used to seamlessly track sales and finances with accounting software integrations such as Xero and Quickbooks. Others can create smooth and automated delivery processes by integrating to delivery platforms like Lalamove, GrabFood, Deliveroo and FoodPanda.
Each POS vendor may have different integrations for their systems, so finding the POS system that suits your needs is crucial.
6. Why should you use a POS system?
If you are running any kind of business that needs to keep track of sales, inventory, customer and other information, a POS system can be an excellent tool to run your business in an efficient, organised manner. More than a cash register, POS software is designed to help you manage your business and scale up as your business grows.
So why should you use a POS system?

7. How much does a POS system cost?
Investing in a POS system is not an easy decision to make, especially when there are many different systems on the market. The cost of a POS system completely depends on the complexity of its software and hardware, the quantity purchased, and the vendor.
The average price for traditional or legacy POS systems can range from $1,000 to $10,000, whereas cloud-based POS systems are typically priced on a subscription basis. These can range from $50 to $500 a month. It’s important to note that these are rough estimates, and the actual price of a POS system will highly depend on factors such as the hardware and software, features required, your type of business, and your specific needs.
However, there are government grants designed to help your business successfully join a data-driven society and upgrade your technology. Additionally, with features designed and enabled to help your business perform more efficiently, reduce costs and grow, a POS system provides an immensely positive return on investment.
8. What types of businesses use POS systems?
There are several industries that can benefit from a POS system. Here are some examples that utilise point-of-sale solutions:

Conclusion
Every business is unique, and with all of the options for POS systems out there, it can be difficult to choose just one that works for your business. When buying a new POS system, it’s always a good idea to consider all of your options. You may decide to get multiple quotes from different vendors, and compare the costs and features before choosing one that fits your budget and needs.
EPOS
If you’re in need of a new Point of Sale system in Singapore, you’re in the right place. For businesses seeking an ultra-seamless POS system that provides precise control and robust data analytics, nothing feels like an EPOS system. EPOS is one of Singapore’s leading POS system vendors, providing powerful features designed to help your business thrive by improving efficiency, reducing costs and increasing profitability. Elevate your business today with EPOS! Get to know our system by signing up for a free, non-obligatory demo.
• Written by Adrija Chakravarti
Was this article helpful?
YesNo



